Description
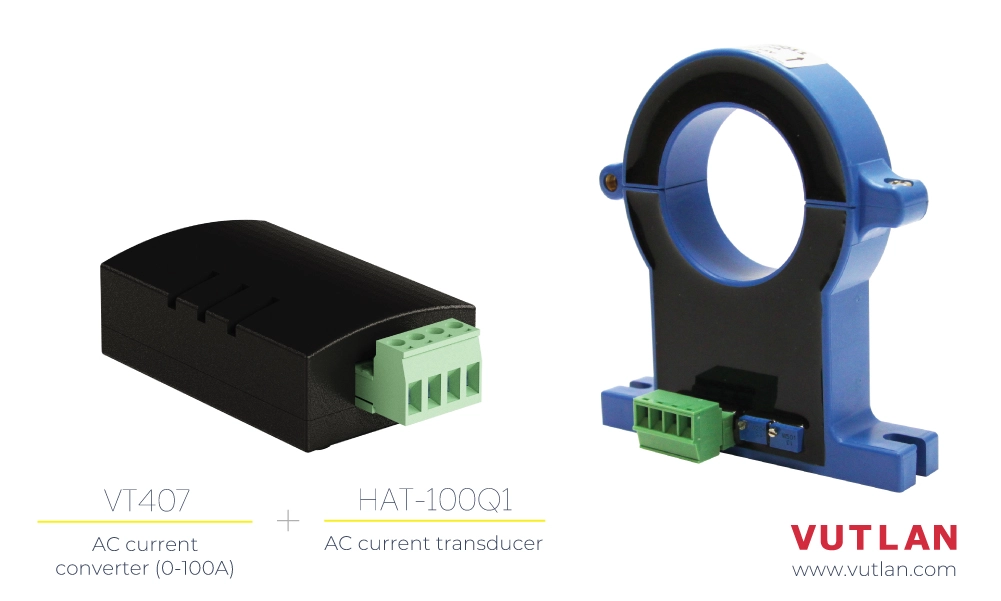
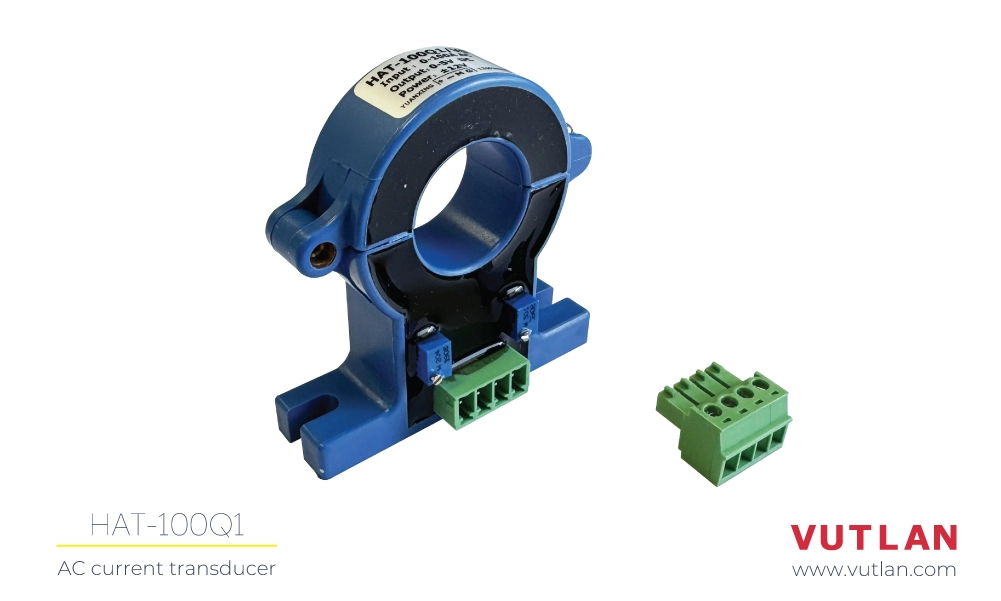
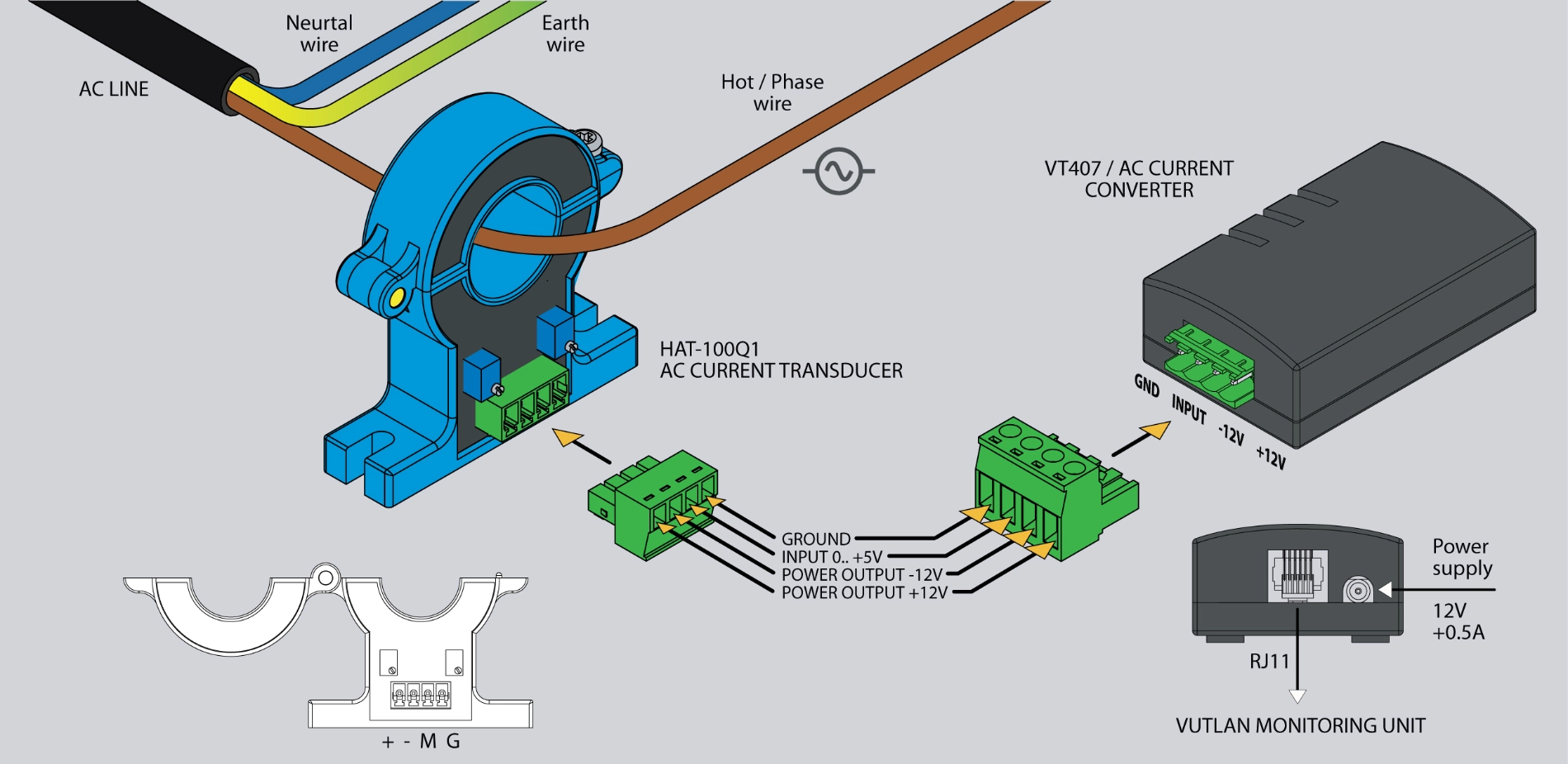
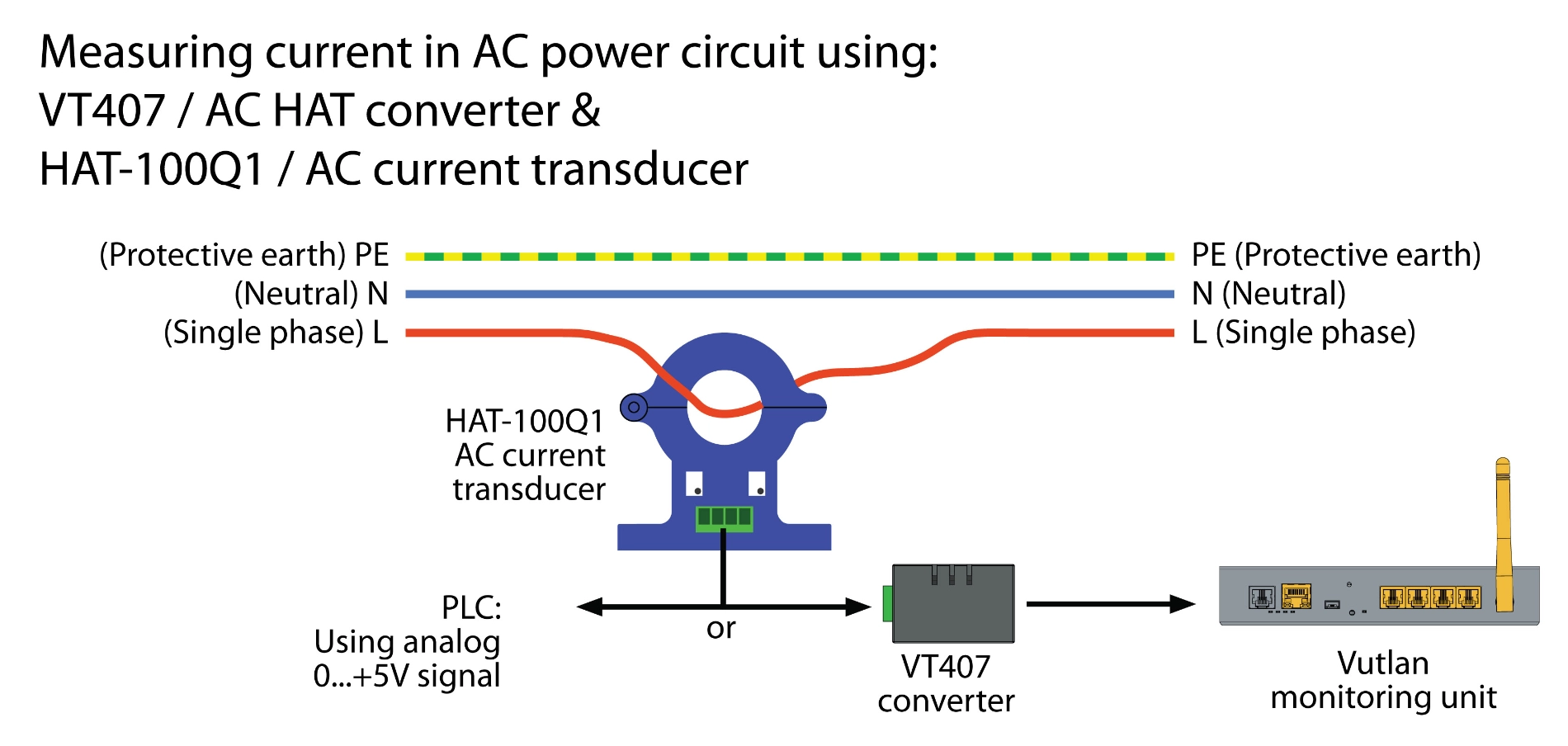
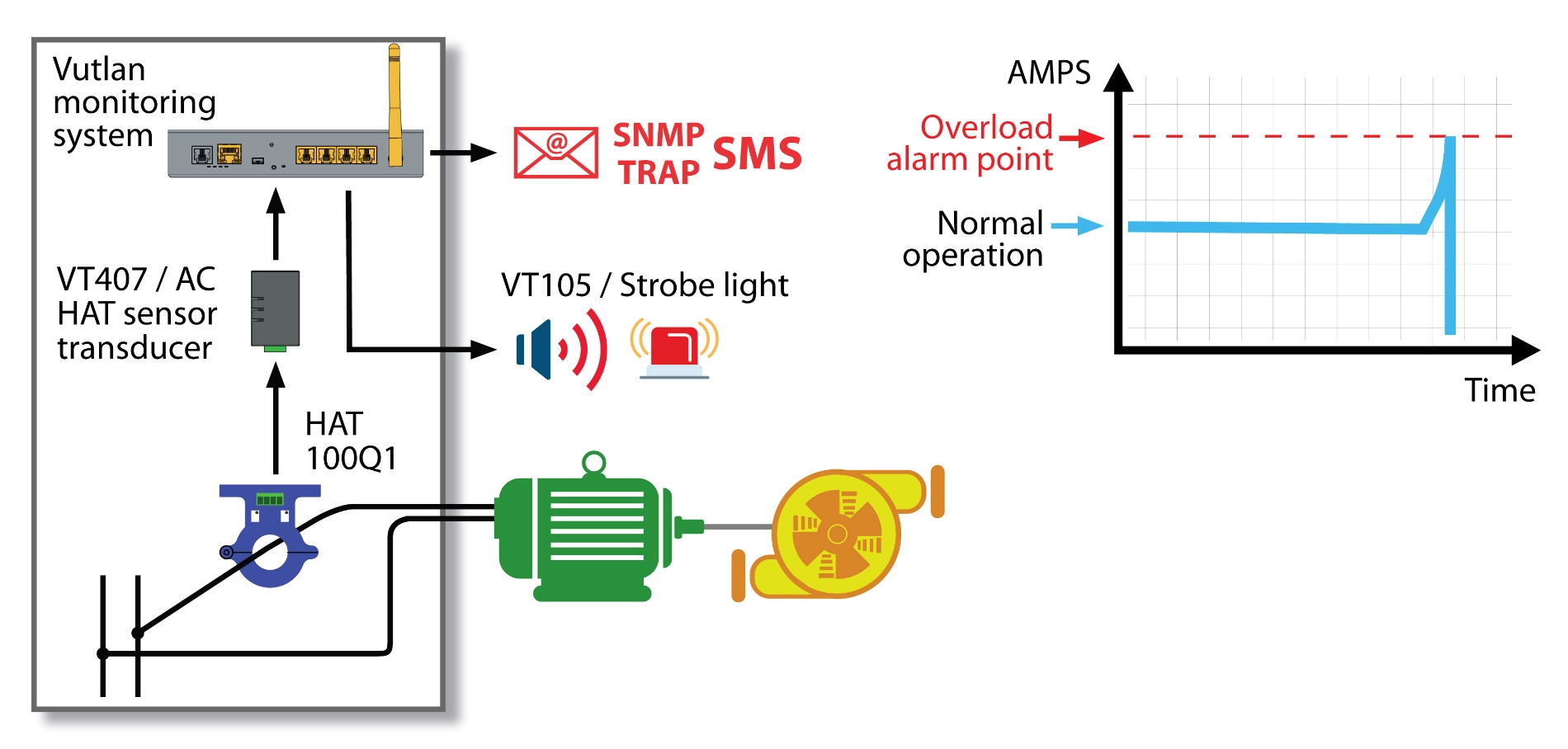
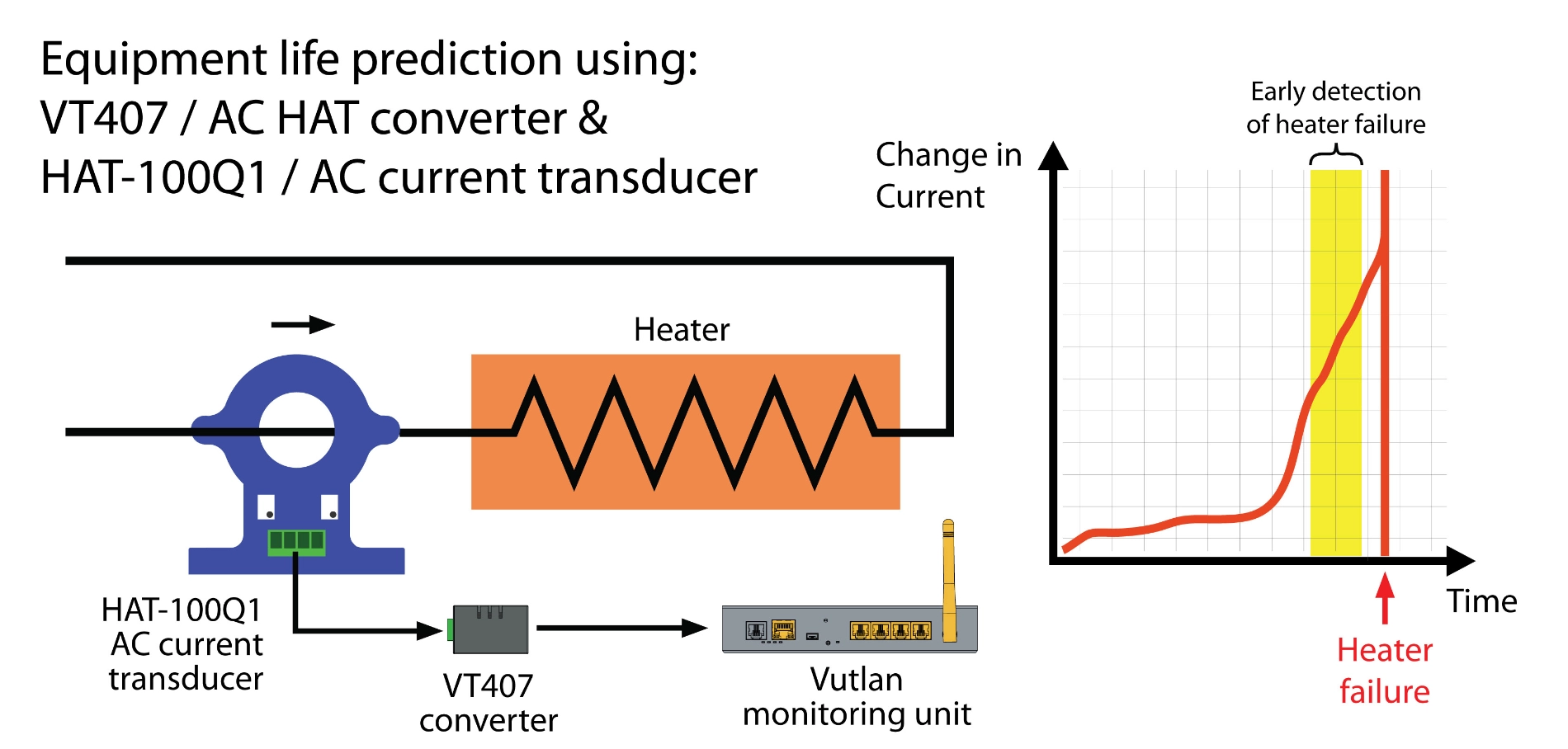
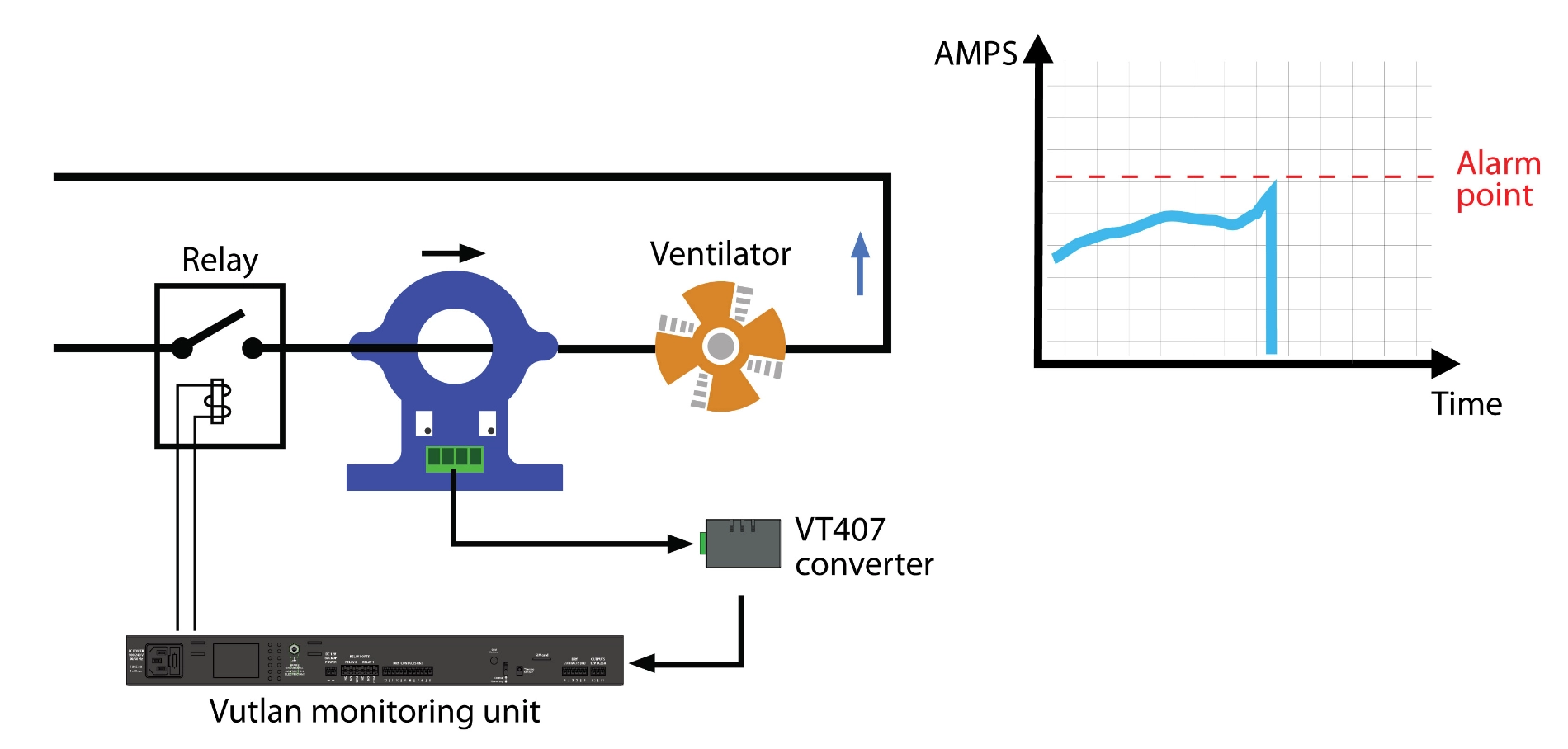
The HAT-100Q1 is a simple open-loop DC ammeter capable of measuring AC current in the 0-100A range. It connects to the monitoring system via the VT407 transceiver.
The VT407 / AC current transceiver transmits measured current data from the HAT-100Q1 AC transducer to the Vutlan monitoring device.
This plug-and-play transceiver easily connects to any analog port of Vutlan monitoring devices.
The maximum amount of sensors can be extended using the VT408 / Sensor extension unit.
Required Components
VT407 AC current converter
VT407 transfers the data received from HAT-100Q1 into Vutlan monitoring system.
Specifications
Sensor type:
AC current transducer
Used for:
Measures AC currents in the range of 0-100A and and send the data in the range 0-5V
Measured AC current:
0-100A
Maxamum distance:
50 meters from the monitoring unit or VT408 extension unit
Outputs:
4 pin terminal, pitch 3.81mm
Operating temperature:
Min. -10° C - Max. 80° C
Operating humidity:
Min. 5% - Max. 95% (Non-Condensing)
Power input:
±12V
Dimensions:
Size 60 × 61 × 16 mm, internal diameter 21mm
Mounting:
Wall mount, hanging
Manufactured in:
China
HS Code:
9030 33 100
GTIN:
8588009886549
Warranty:
90 days
Use cases
- Real-time AC monitoring: Monitor current to prevent overload or failure of electrical equipment.
- Power Monitoring: Monitors the current flowing through telecommunications equipment to ensure stable and reliable power supply.